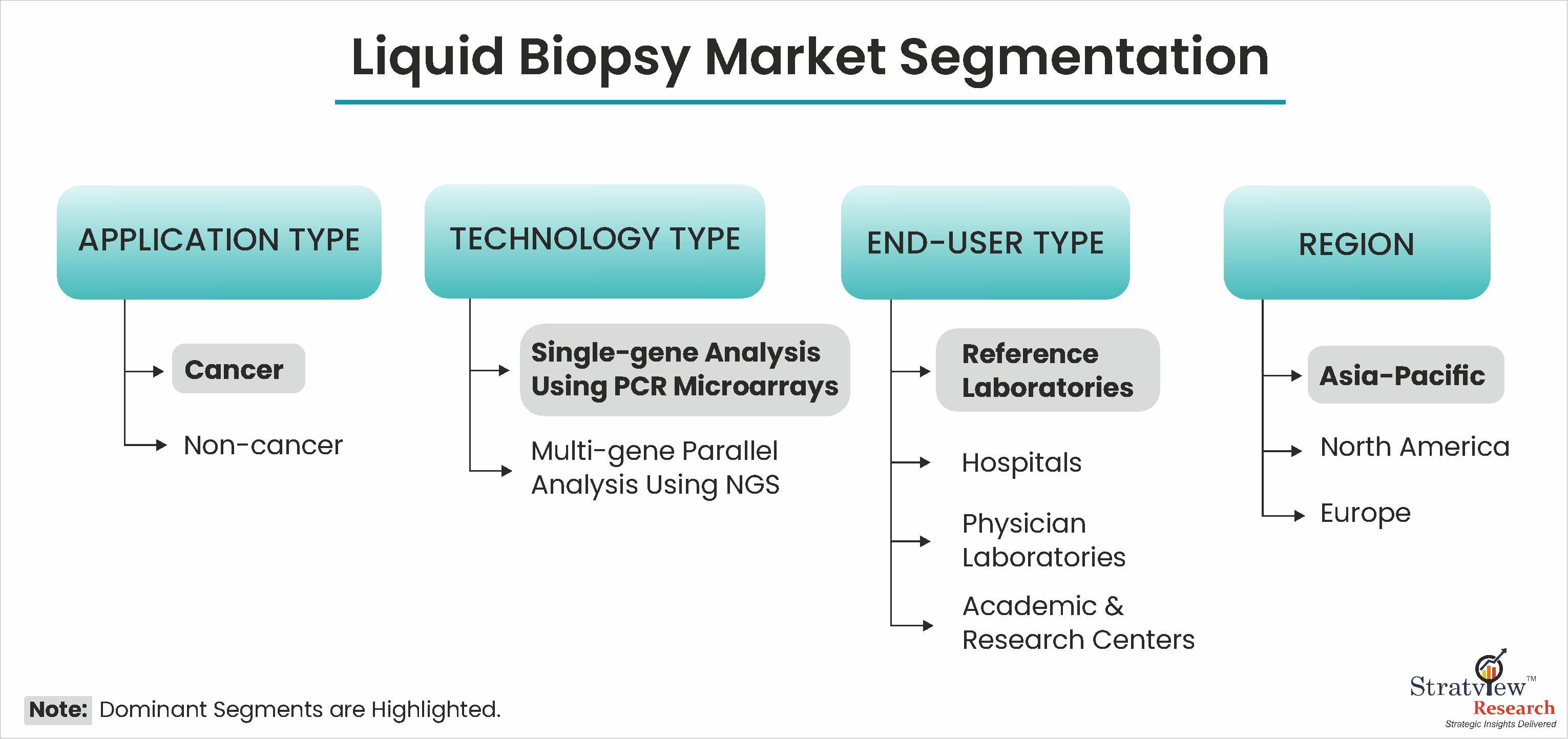
According to Stratview Research, the liquid biopsy market was estimated at USD 2.83 billion in 2022 and is likely to grow at a CAGR of 17.99% during 2023-2028 to reach USD 7.64 billion in 2028.
In the realm of modern medicine, the liquid biopsy market is akin to discovering a treasure trove of invaluable insights. Dubbed as "liquid gold," these minimally invasive diagnostic tests offer a wealth of information by analyzing biomarkers present in bodily fluids, revolutionizing the way we detect and monitor diseases, particularly cancer. In this article, we embark on a journey to navigate the remarkable growth and potential of the liquid biopsy market.
A Golden Opportunity for Non-Invasive Diagnostics:
Traditional methods of diagnosing diseases often involve invasive procedures, posing risks to patients and limiting accessibility. Liquid biopsies, however, offer a golden opportunity to overcome these limitations. By analyzing circulating biomarkers such as cell-free DNA (cfDNA), circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA), and exosomes found in blood, urine, and other bodily fluids, liquid biopsies provide a non-invasive and accessible alternative for disease detection and monitoring.
Cancer Detection: Pioneering the Way:
Cancer detection stands at the forefront of liquid biopsy applications. Liquid biopsies have emerged as powerful tools for early cancer detection, allowing healthcare providers to detect genetic alterations associated with tumors at an early stage, often before symptoms manifest. Additionally, liquid biopsies enable real-time monitoring of disease progression, treatment response, and the emergence of resistance, empowering oncologists to tailor treatment strategies for better outcomes.
Navigating Growth Drivers:
The growth of the liquid biopsy market is propelled by a myriad of factors. Advances in technology, such as next-generation sequencing (NGS), digital PCR (dPCR), and single-cell analysis, have significantly enhanced the sensitivity and specificity of liquid biopsy tests, enabling the detection of rare mutations with unprecedented accuracy. Moreover, the rising prevalence of cancer, coupled with increasing awareness about the benefits of early detection, is driving the demand for liquid biopsy-based screening and monitoring.
Expanding Horizons Beyond Oncology:
While oncology remains a primary focus, the applications of liquid biopsy extend beyond cancer diagnostics. Liquid biopsies hold promise for diagnosing and monitoring a range of other diseases, including infectious diseases, autoimmune disorders, and prenatal screening. In infectious disease diagnostics, for example, liquid biopsies can detect viral RNA or DNA in blood samples, enabling rapid and accurate diagnosis of infections such as HIV, hepatitis, and COVID-19.
Navigating Challenges on the Path to Success:
Despite its immense potential, the liquid biopsy market faces challenges that must be navigated for continued growth and adoption. Standardization of sample collection and analysis protocols, validation of biomarkers, and regulatory considerations are among the key challenges. Additionally, reimbursement policies and cost-effectiveness must be addressed to ensure widespread accessibility and affordability of liquid biopsy tests.
Charting the Course for the Future:
As we navigate the growth of the liquid biopsy market, collaboration among stakeholders is essential for overcoming challenges and unlocking the full potential of this transformative technology. Continued investment in research and development, collaboration between industry players and regulatory agencies, and education initiatives to raise awareness among healthcare providers and patients will be critical in shaping the future of liquid biopsy diagnostics.
In conclusion, liquid biopsies represent a golden opportunity in the field of diagnostic medicine, offering non-invasive, accessible, and informative tools for disease detection and monitoring. By navigating the growth of the liquid biopsy market, we can harness the full potential of this "liquid gold" to improve patient outcomes, advance precision medicine, and revolutionize the way we diagnose and treat diseases.